|
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||
public interface ClientServerIntegration
DataSources
First you
must create DataSources that describe the objects from your object model
that will be loaded or manipulated within your application. All of Smart GWT's most powerful functionality builds on
the concept of a DataSource, and because of Smart GWT's databinding framework (see DataBoundComponent), it's as easy to create a DataSource that can configure an unlimited
number of components as it is to configure a single component.
For background information on how to create
DataSources, bind components to DataSources and initiate DSRequests, please see the Data Binding chapter of the Smart GWT Quickstart
Guide.
Data Integration
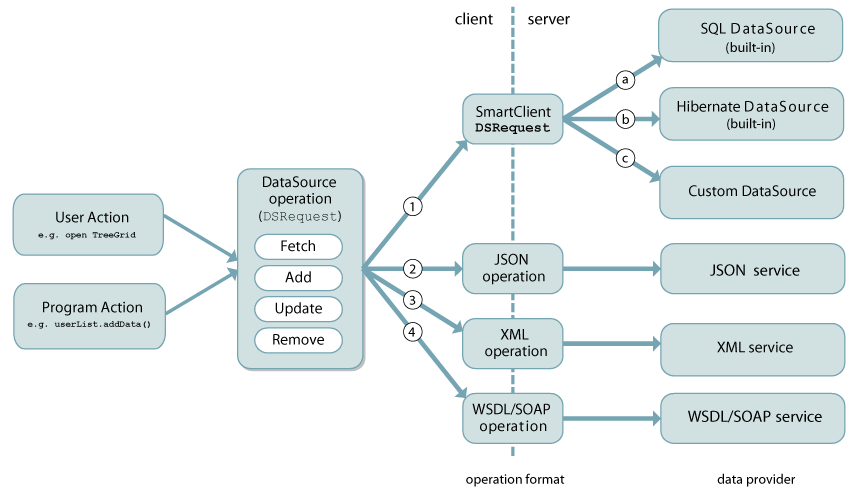
DataSources provide a data-provider agnostic API to Smart GWT Visual Components that allow them to perform the 4 CRUD operations (Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete). By "agnostic" we mean that the implementation details - the nuts and bolts of how a given DataSource actually retrieves or updates data - are unknown to bound Smart GWT components. One effect of this is that DataSources are "pluggable": they can be replaced without affecting the User Interface.
When a visual component, or your own
custom code, performs a CRUD operation on a DataSource, the DataSource creates a DSRequest (DataSource Request) representing the operation. "Data Integration" is the process
of fulfilling that DSRequest by creating a corresponding DSResponse (DataSource
Response), by using a variety of possible approaches to connect to the ultimate data provider.
There are two main approaches to integrating DataSources with your server technology:
Client-side integration: DataSource requests arrive as simple HTTP
requests which your server code receives directly (in Java, you use the Servlet API or .jsps to handle the requests).
Responses are sent as XML or JSON which you directly generate. 
Smart GWT supports, out of the box, codeless connectivity to various kinds of common data providers, including SQL and Hibernate. Smart GWT also provides functionality and tools for accelerated integration with broad categories of data providers, such as Java Object-based persistence mechanisms (JPA, EJB, Ibatis, in-house written systems), and REST and WSDL web services in XML or JSON formats. Ultimately, a DataSource can be connected to anything that is accessible via HTTP or HTTPS, and also to in-browser persistence engines such as Google Gears.
Choosing a Data Integration Approach
This section aims to help you decide which of the many possible data integration approaches is best for your particular circumstances. The recommendations given here will guide you to the approach that involves the least effort.
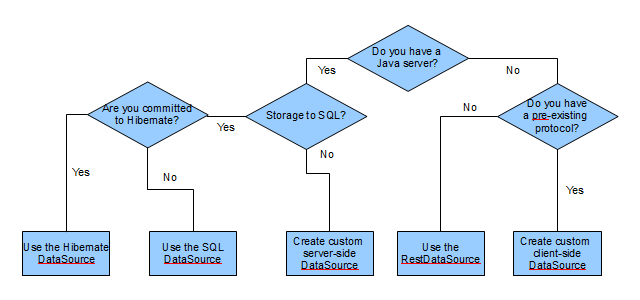
SQLDataSource vs
JPA/Hibernate in order to understand the large benefits the SQLDataSource providesautoDeriveSchema feature, or from Java Beans
via the schemaBean feature. Or, use the Admin Console to generate tables from DataSource definitions you create
by handschemaBean
feature to derive DataSource definitions from any Java beancustom DataSource that provides the CRUD operations you want
to support.DMI, or any combination of the two: OperationBinding
allow you to dynamically set data values at transaction-processing time, using built-in Velocity supportvalidate() method of
the DataSource to provide extra custom validations - just call super to obtain the list of errors
derived from Smart GWT validations, then add to that list as required with your own custom codeexecute() method of the DataSource to add extra processing either before or
after the Smart GWT processingSQL Templating to change, add to or even completely replace the SQL
sent to the database, and to implement special query requirementscustom HQL queries to implement special
query requirementsthe server integration overview. RestDataSourceclient-side data integration features to create a custom
client-side DataSource that adapts the DataSource protocol to your existing services
RPCs: Unstructured Server Communication
Smart GWT also supports "unstructured" client-server
operations. These RPCRequests (Remote Procedure Call Requests) are a low-level, very
flexible mechanism for custom client-server communications. In an nutshell, RPCRequests:
RPCManager.send), and have their responses handled by custom code (the callback passed to send()) RPCRequests are relatively rare. Most client-server communications are better done in a structured fashion using a
DSRequest (DataSource Request). Note that any RPCRequest can alternatively be
framed as a DataSource fetch; depending on the circumstances,
this may be more convenient.
See the RPCManager documentation for further
information on RPCRequests.
|
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||